Sketches (3.9.2011) (2012)
Materials
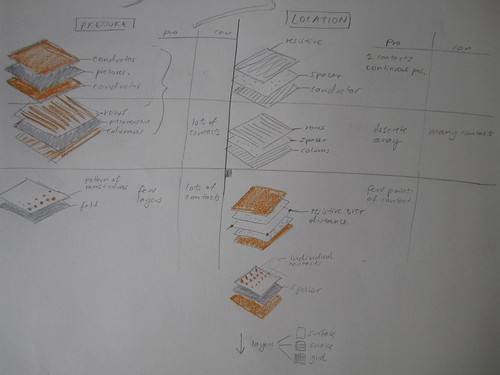
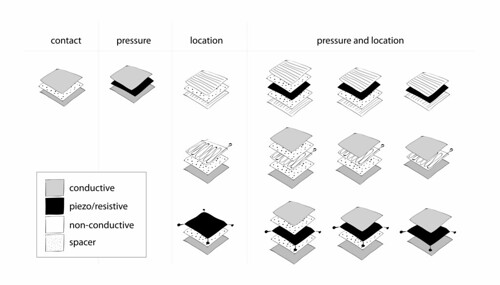
This sketch shows some of the variations of pressure and location sensors made by layering conductive and piezo/resistive materials. Piezoresistive materials change electrical resistance under mechanical stress (pressure, bend, stretch…). When i refer to resistive materials, i normally mean materials that have increasing resistance over distance. While resistive materials don’t necessarily have piezoresistive properties, piezoresistive materials are normally also resistive. Most of the piezoresistive materials i’ve worked with are piezoresistive only in their z-axis (through the material) and not in their x/y-axis (across their surface). So i am hoping that it will be possible to use such a piezo/resistive material, to measure both change in pressure as well as location.
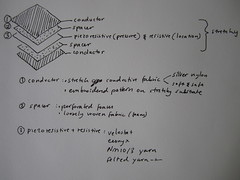
Conductive material: stretch conductive fabrics (silverized nylon, soft and safe…), conductive threads
Resistive materials: resistive thread from LessEMF, resistive yarn from Plug and Wear
Piezo/resistive materials: Velostat, Eeonyx fabrics
Spacer materials: perforated foam, loose woven fabrics, silicon dots…
Non-conductive/isolating materials: jersey fabric….
Resolution
While using a row and column grid/matrix structure within the layering to determine position can be very accurate, one accumulates a lot of contacts and resolution is limited by the number of contacts one is willing or able to include. Having a continuous, resistive surface or space-filling curve reduces the number of contacts to three or less. Because it is not made up of discrete points, resolution depends on reliably one can detect differences in distance.
Non-linearity
Most piezo/resistive materials are not linear in their resistive changes (distance/stress). Mapping the resistance values from the sensor skin to a model will definably also play a roll in how well the data appears.
Setup
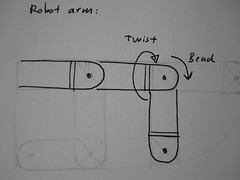
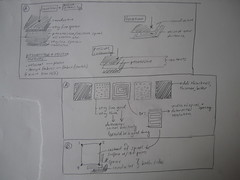
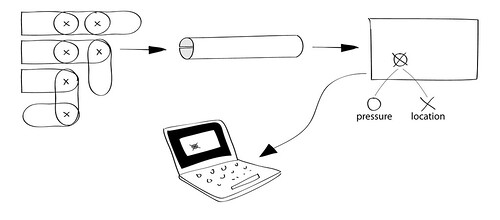
Here is a sketch of the very basic setup and idea. The robotic arm (with two joints) which can bend and twist should be covered in a textile skin. The skin will most likely be a stretchy fabric tube that fits snugly over the robot arm. For simplicity of construction, the tube is folded rectangle, consisting of various layers of conductive, resistive, piezoresistive and isolating materials.
Data from the robot skin is sent to a computer application that visualizes sensor data.
Brainstorming